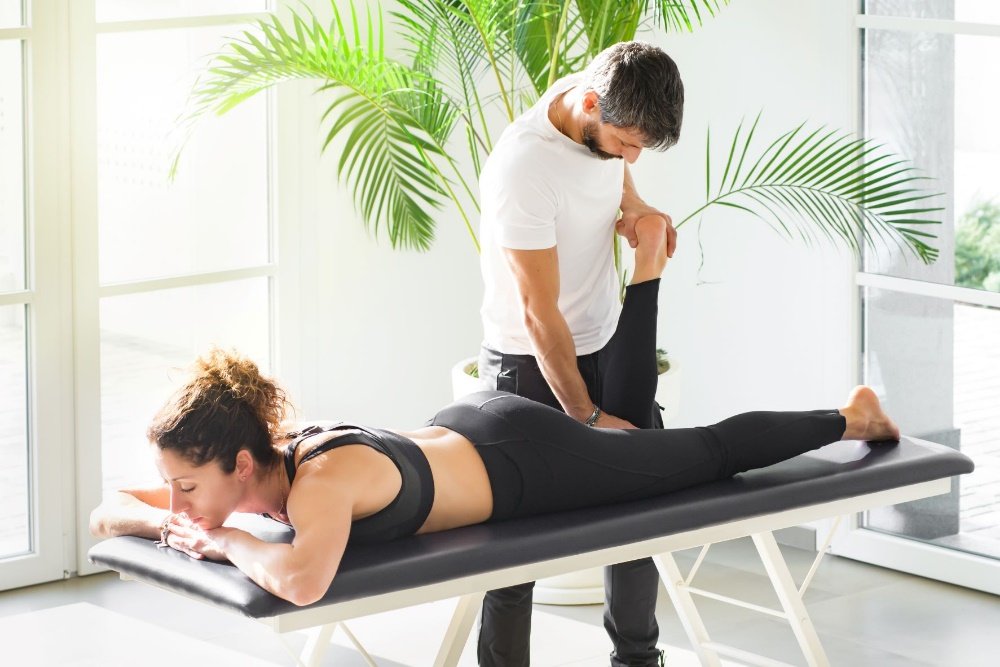

Meniscus Tear Rehab: Your Path to Full Recovery.
Understanding Meniscus Injuries and the Role of Physiotherapy in Manchester
Meniscus injuries can cause significant discomfort, pain, and anxiety for patients, who often worry about their ability to return to their previous lifestyles. However, physiotherapy in Manchester City Centre offers effective solutions for healing and managing knee injuries, particularly meniscus tears. Through personalized treatment plans, physical therapy enhances knee function, reduces pain, and promotes recovery, providing valuable insight into the benefits of physical therapy for meniscus injuries.
Understanding Meniscus Injuries and the Role of MY Sports Physiotherapy
Meniscus injuries are common among individuals who engage in activities involving twisting, pivoting, or sudden stops. These injuries can lead to significant discomfort and pain, often causing anxiety about one’s ability to return to previous levels of activity or sport. In Manchester, where a diverse population participates in various physical activities, understanding the nature of meniscus injuries and the role of physiotherapy in recovery is crucial for effective management and rehabilitation.
Anatomy of the Meniscus Knee Joint
The knee joint consists of two menisci—medial and lateral—made of fibrocartilage. These crescent-shaped structures serve several critical functions:
- Shock Absorption: Menisci absorb impact forces during weight-bearing activities, protecting the articular cartilage from damage.
- Joint Stability: They help improve the fit between the femur and tibia, contributing to joint congruence and overall stability.
- Force Distribution: The menisci distribute load across the knee joint, reducing the risk of injuries to the surrounding ligaments and cartilage.
- Facilitation of Movement: Menisci play a vital role in allowing smooth motion within the knee joint, enabling activities such as walking, running, and jumping.
Causes and Symptoms of Meniscus Injuries
Meniscus injuries are prevalent and can affect individuals across various age groups and activity levels. Understanding the causes and symptoms associated with meniscus tears is essential for early identification and effective management.
Causes of Meniscus Injuries
- Acute Injuries:
Acute meniscus tears typically occur due to sudden, traumatic events. Common scenarios include:- Twisting Motions: Sports that involve rapid direction changes (e.g., basketball, soccer, football) can lead to twisting of the knee while the foot remains planted.
- Direct Impact: A blow to the knee during contact sports can cause tears in the meniscus.
- Sudden Stops: Quick stops or changes in speed can strain the knee, leading to tears.
- Degenerative Changes:
Degenerative meniscus tears develop over time, often as a result of wear and tear on the knee joint. Factors contributing to this type of injury include:- Aging: As individuals age, the menisci can become weaker and less resilient, making them more susceptible to tears even during normal activities.
- Chronic Conditions: Conditions such as osteoarthritis can contribute to degenerative changes in the meniscus, increasing the likelihood of tears.
- Repetitive Stress: Repetitive knee motions (e.g., in certain occupations or sports) can lead to cumulative damage to the meniscus.
- Risk Factors:
Several risk factors can increase the likelihood of meniscus injuries:- High-Impact Sports: Athletes participating in high-impact or pivot-heavy sports are at greater risk.
- Previous Knee Injuries: A history of knee injuries can predispose individuals to future meniscus tears.
- Obesity: Excess body weight places additional stress on the knee joint, increasing the risk of injury.
Symptoms of Meniscus Injuries
Individuals with a meniscus tear may experience a variety of symptoms, which can vary in severity. Common symptoms include:
- Knee Pain:
- Pain is typically localized around the knee joint and may be aggravated by twisting, squatting, or other weight-bearing activities.
- Swelling and Stiffness:
- Swelling often develops within a few hours of the injury, resulting in stiffness and reduced mobility in the knee joint.
- Limited Range of Motion:
- Patients may find it difficult to fully extend or flex their knee, impacting their ability to perform daily activities.
- Popping or Clicking Sensation:
- A characteristic symptom of a meniscus tear is a popping or clicking sound during movement, often referred to as “crepitus.”
- Difficulty Bearing Weight:
- Individuals may experience difficulty or discomfort when trying to bear weight on the affected leg, leading to compensatory movements or altered gait patterns.
Diagnosis
A thorough assessment by a healthcare professional, including a detailed medical history, physical examination, and imaging studies (such as MRI), is essential for diagnosing a meniscus tear. Identifying the location and extent of the injury will guide treatment options.
The Role of Physiotherapy in Recovery
Physiotherapy plays a pivotal role in the rehabilitation of meniscus injuries. The primary goals of physiotherapy are to reduce pain, restore function, and enhance overall knee stability. Here’s a more in-depth look at the key components of physiotherapy management for meniscus injuries:
The knee joint is one of the most commonly injured joints, primarily due to its role in supporting body weight and its unique biomechanical characteristics. The menisci—two crescent-shaped fibrocartilages located between the femur and tibia—are crucial for maintaining joint congruence, stability, and proper function. They help distribute forces across the knee, enhancing stability and facilitating movement. In cases of a meniscus tear, a physiotherapeutic approach combining physical therapy and sports massages in Manchester becomes essential for returning to daily activities and sports.
Causes and Risk Factors for Meniscus Injuries
Meniscus tears are prevalent, particularly among athletes engaged in sports requiring twisting, pivoting, or sudden stops. Approximately 50% of meniscus and ligament injuries occur in athletes, with a prevalence of around 12% to 14% in the general population. Aging also contributes to the risk, as degenerative changes in cartilage can lead to tears even with minimal trauma.
Trauma from sudden knee twists or hyperflexion/hyperextension can cause meniscus injuries. This risk is heightened in activities such as soccer, basketball, and tennis, where rapid changes in speed or direction are common. Moreover, anatomical abnormalities, such as varus or valgus knees, can increase susceptibility to meniscus damage.
Complications and Treatment Options for Meniscus Injuries
Meniscus tears, if not addressed appropriately, can lead to various complications that may impact the knee’s function and overall joint health. Understanding these complications and available treatment options is vital for effective management.
Complications of Untreated Meniscus Tears.
Meniscus tears can cause fluid accumulation in the knee joint (effusion), leading to swelling, discomfort, and stiffness. Persistent effusion may require medical intervention.
Knee Instability:
Without proper treatment, a meniscus tear can lead to knee instability, causing the joint to feel wobbly or “giving way.” This instability can affect balance and coordination, increasing the risk of falls and further injuries.
Chronic Pain:
Untreated meniscus tears often result in ongoing pain, which may worsen over time. This pain can interfere with daily activities and limit mobility, significantly affecting the quality of life.
Loss of Range of Motion:
The presence of a meniscus tear may restrict the knee’s range of motion. If not treated, scar tissue may develop, further limiting movement and function.
Osteoarthritis:
One of the most significant long-term risks associated with untreated meniscus tears is the development of osteoarthritis. The menisci play a crucial role in distributing weight and absorbing shock in the knee joint. Damage to these structures can lead to uneven wear on the cartilage, resulting in joint degeneration and chronic arthritis.
Joint Effusion:
The Role of Physical Therapy Early Stage Exercise Rehabilitation in Recovery Process
Physical therapy in Manchester is an effective, non-invasive treatment option for meniscus injuries. It aims to:
- Avoid Surgery: Many meniscus tears can be managed effectively without surgical intervention. Research shows that physical therapy is often a first-line treatment for these injuries, and surgery may only be necessary if significant instability or pain persists.
- Manage Pain: Physiotherapy helps reduce knee pain through targeted exercises and education on pain management strategies.
- Regain Mobility: Through specific techniques, physical therapy restores the range of motion and function in the knee.
- Strengthen the Knee: Exercises prescribed by physiotherapists strengthen muscles supporting the knee joint, reducing the risk of future injuries.
- Enhance Quality of Life: By facilitating recovery and promoting mobility, physical therapy helps patients return to their daily activities and sports without discomfort.
Exercises for Meniscus Injuries
While it’s essential to rest from activities that caused the injury, certain exercises can aid in recovery. Here are some recommended exercises:
- Calf Stretch: Strengthens the knee and promotes flexibility.
- Knee Extension: A low-impact exercise that supports knee rehabilitation.
- Thigh Stretch: Particularly effective for medial meniscus tears.
- Pelvic Lift: Engages the core and supports knee function.
- Heel Lift: A gentle exercise that aids recovery with minimal discomfort.
How Long Does It Take to Heal?
Typically, recovery from a meniscus tear treated with physical therapy in Manchester takes between 4 to 8 weeks, depending on the injury’s complexity. Compliance with a tailored rehabilitation program significantly enhances recovery outcomes.
Preventing Meniscus Injuries
While not all meniscus injuries can be predicted, certain preventive measures can help reduce risk:
- Regular Exercise: Aim for at least 30 minutes of activity, focusing on strengthening muscles around the knee.
- Warm-Up and Stretch: Essential before and after physical activity to maintain flexibility.
- Proper Footwear: Invest in shoes with good support, especially for sports.
- Posture and Back Care: Maintain proper posture to avoid undue stress on the knees.
- Nutrition: A balanced diet supports musculoskeletal health and improves recovery.
Conclusion
At our Sports Injury Clinic in Manchester, we are dedicated to helping you recover from meniscus injuries effectively and affordably. With a comprehensive approach to rehabilitation through physical therapy, you can avoid the need for surgery, manage pain, and regain your knee’s function. If you have a meniscus injury or wish to prevent one, book an appointment with our expert physiotherapists today by clicking here.
What Function Does the Meniscus Have?
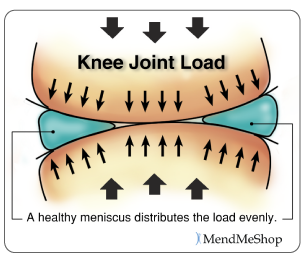
Meniscus Function for Shock Absorbance
being the stabilizers of the knee and those that distribute the synovial fluid inside it. Thus, they are two elements that support and resist a large compression load (Alice J. S. Fox et la, 2012).
How Does a Meniscus Injury Occur? And Which People Are More Exposed to Suffering From it?
We speak of a meniscus injury when there has been a tear, rupture or displacement of said cartilage, which usually happens more internally than externally. It is a frequent injury and occurs more in men than in women (B E Baker et la, 1985).
The Meniscus Can Be Injured at Any Age and For Various Reasons
Due to trauma from movements that involve a sudden twist of the knee (such as sudden pivoting or sudden braking and turning). These gestures are associated with sports practice in young people. For example, when playing soccer, basketball, or tennis, there are sudden changes in speed or you put your weight on one foot and then forcefully rotate your knee.
Those movements in which there is a sudden hyperflexion or hyperextension of the knee, kneeling, lifting or squatting or lifting something heavy, can also damage it. In people of a certain age, the degenerative phenomena suffered by the cartilage may be the cause of its breaking with these minimal traumas or even without trauma. And it is that age is one of the factors that increases the risk of meniscus tear, due to wear.
Some alterations or deformities that certain people present in the anatomical arrangement of the knees (varus or valgus knees, for example) make them more prone to wear of the menisci due to overloading them.
What Symptoms Does Knee Meniscus Injury Cause?
When the meniscus injury occurs, the joint hurts with variable intensity depending on aspects such as the size, type of tear, or the mechanism that caused it (if it is a trauma, the pain usually has a more acute character than what happens when the meniscus is injured). meniscus wears progressively until it breaks). The pain can be located at different points, although, in general, it is located in the injured meniscus at the specific moment in which the tear occurs.
- Also, the knee swells or inflames (it can even bruise) and becomes stiff. On occasions, it can be totally or partially blocked (it is the sensation of having the knee locked when you try to move it) or notice difficulty in fully extending it. Meniscus crunches can also appear, although if they are not accompanied by pain, that is, they are isolated, they should not alarm us.
At My Sports Injury Clinic we help you take care of your health to prevent this type of injury and maintain your quality of life. If you have any type of ailment related to the meniscus, do not hesitate to request an appointment with our experts in physical therapy and manual therapy in Manchester and we will help you solve it, click the following link to book an appointment https://mysportinjury.janeapp.co.uk/
What Are the Complications & How is The Knee Meniscus Injury Treated?
Can Physical Therapy Help Knee Injuries?
Over time, a meniscus tear can become complicated and make the affected knee unstable or limit its movement. Likewise, it can cause chronic pain and the chances of suffering osteoarthritis in the joint in the future increase. Therefore, it is necessary to choose and start the most appropriate treatment as soon as possible, which will depend on the type, size and location of the lesion, as well as the patient’s age and activity level.
Initially, the doctor and physio in Manchester must assess and indicate the most appropriate course of action.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may be added to relieve pain and reduce swelling. A physiotherapy program in Sports Injury Clinic is also necessary, which will include exercises to increase the flexibility and strength of the knee and the muscles around it, which will increase its stability.
The treatment plan for a Knee Meniscus Tear involves tailored physiotherapy sessions that encompass various approaches. Manual therapy in Manchester is employed to alleviate pain, drainage techniques help remove inflammatory fluid, joint techniques enhance mobility, and exercises aim to bolster muscle strength. Rehabilitation exercises target muscle strength and proprioceptive exercises enhance balance and body awareness. Additionally, balance exercises and gait reeducation are incorporated to optimize the overall treatment process. This comprehensive approach ensures effective recovery and improved knee function.

In addition, a series of conservative measures must be taken consisting of the following.
Rest: rest, try not to walk and avoid sports or any activity in which you lean on the knee, turn it or flex it, for the period of time that your doctor advises.Ice: in order to reduce inflammation and reduce pain, apply cold to the affected area for forty-eight hours after the injury.Compression: depending on the degree of severity of the injury, a bandage, a knee pad or a splint can be placed.Elevation: when you are sitting or lying down, keep the affected extremity elevated.
If Surgery for Torn Meniscus is Needed, How Long Will the Recovery Time Frame Be?
It is pointed out that elite athletes are likely to return to sports activities from 4 up to 6 months after undergoing surgical intervention, according to (Tammam Hanna et la, 2022).
What is the Expected Time Frame to Recover from a Torn Meniscus Dealt with Physical Therapy in Manchester?
Regularly this rehab process of Torn Meniscus Injury treated with Physical Therapy will range from 6 up to 8 weeks. It should be noted that this will only be able to come about with the guidance of a top-notch physical therapy rehab and a suitable reduction of sporting activities. Conservative management / Physical Therapy is the best treatment option for meniscus injuries but when the symptoms of locking, giving way, or significant instability, are not presented, (according to HealthLine).
How Can I Avoid Meniscus Injuries?
The vast majority of meniscus injuries are very difficult to predict, since they occur when the knee is turned suddenly on a stationary foot.
The recommendations to prevent this type of injury include limiting just a bit, physical activity and demanding training, but also carrying out exercises that increase muscle mass in that area so this area will be the one which absorbs the greatest impact of the exercise, so by doing this way, the weight does not affect that much the menisci.
5 Tips to Prevent Meniscus Injuries and Knee Problems
Although in the previous paragraph we have already indicated some keys to prevent this type of annoying injury/ knee problems, we now detail a series of tips that will help you avoid these ailments.
Exercise regularly! 30 minutes is reccommended by Physiotherapists
But avoid aggressive knee poses like deep squats and heavy weights. To avoid this type of injury, it is advisable to strengthen the leg muscles that help stabilize and protect the knee.
Don’t forget about warming up and stretching
Training is important, but it is also important to warm up your body beforehand and stretch it after physical work, especially if the legs are involved.

Wear the right footwear
When you do sports you should wear the right shoes, especially with good foot support and good heel support. Likewise, it is key that you learn and use the appropriate techniques for the sport you practice, so you will always avoid injuries of all kinds.
Take care of your back
An imbalance in the lower back or pelvis will cause a knee to be working in a bad posture and this will lead to wear and tear or even early osteoarthritis.
Watch your diet
This seems like a wild card for everything we do in our lives, but it is true that it is important to protect our musculoskeletal system. Look for a diet that does not cause calcifications and that allows the knee to have a better blood supply so that it stays in good condition for more years.
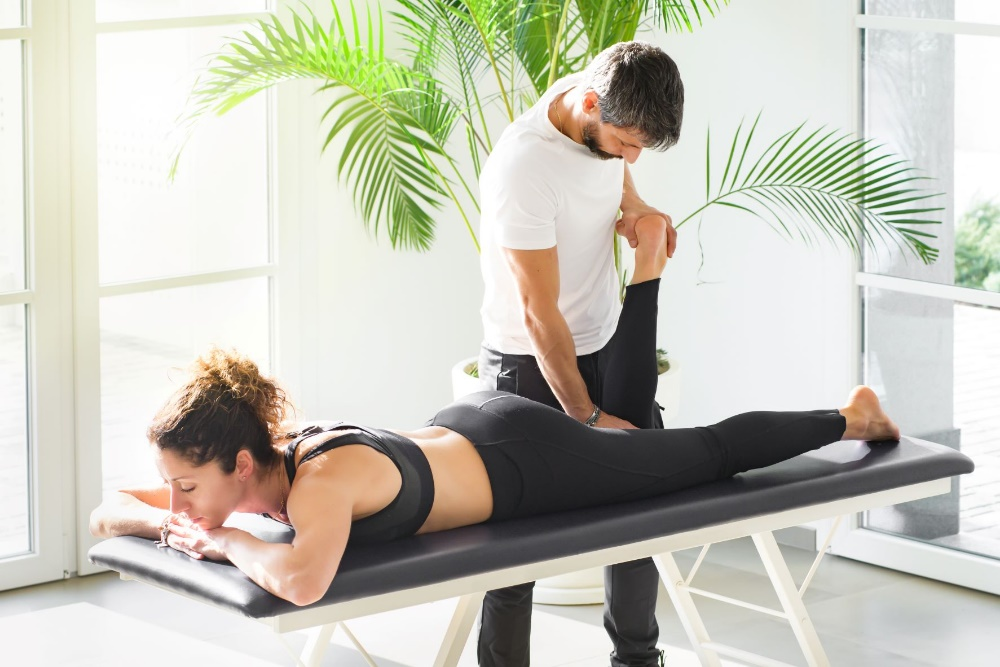

Benefits of Physical Therapy in Manchester City for Knee Meniscus Tear and Knee Injuries
If the thought of undergoing surgical procedure for a meniscus injury freaks you, don´t worry because at our Sports Massages Centre in the heart of Manchester City we provide really good news; as non-conservative management is not always the answer to treat Meniscus Tear!
Therefore, Physical therapy is a greatly effective and secure way to pull through a Meniscus Tear and get back to your daily life without difficulty and discomfort.
Let’s look at the benefits of undergoing Physical Therapy in Manchester City for a Meniscus Injury.
Avoid Surgery
Having surgical management is expectedly fearful, especially for patients´ finances. When looking at the costs of non-conservative treatment and comparing to physical therapy in Manchester, the latter has been proven to be way too more accessible and affordable.
Furthermore, it is known that some surgical interventions might be difficult for the body to recover from. Research indicates that in several cases, invasive surgical procedures are ineffective for meniscus tears, as they tend to fail to succeed. So, your physician will most likely recommend Physical Therapy in Manchester as first treatment option for Meniscus Tear.
If persistent pain or lack of improvement occurs despite physical therapy, surgical intervention might become necessary. However, even if you opt for surgery to address your meniscus injury, the importance of physical therapy remains. Post-surgery, continuing with physical therapy in Manchester is essential to support your recovery journey, rehabilitate the affected area, and restore optimal function and mobility. This holistic approach ensures the best possible outcome for your injury management.
Manage Pain
One of the many aims of physical therapy is to reduce, soothe, or eradicate knee pain. Performing a thorough physical clinical examination will help your physical therapist in Manchester to develop a treatment plan for Meniscus Tear Injury.
Besides, the exercise regimen you will be assigned to, you will also be widely taught on pain management.
Regain Mobility
Another principal aim of physical therapy is to improve and restore your range of motion by conducting physical therapy techniques.
Exercises and Stretches for Knee Meniscus Tear and Knee Problems
Exercises for meniscus injuries are recommended by various physiotherapy professionals in Manchester as they are of great help to strengthen this part of the body and promote its rapid recovery.
Of course, this does not mean that you can play sports with a torn meniscus, it is important to rest from the physical activity that caused the injury. The recovery time must combine rest with some exercises for a meniscus tear that must be ordered by a professional.
However, so that you are fully informed before attending the appointment, we will talk about the exercises to strengthen the torn meniscus. That is, the appropriate exercises for this type of injury and that are usually the most recommended by professionals. That way you will have a complete idea of what you can be commissioned to do.
Calf Stretch
Calf stretches are one of the most recommended exercises for a torn meniscus. With a routine that includes this exercise, this part of the knee can be effectively strengthened.
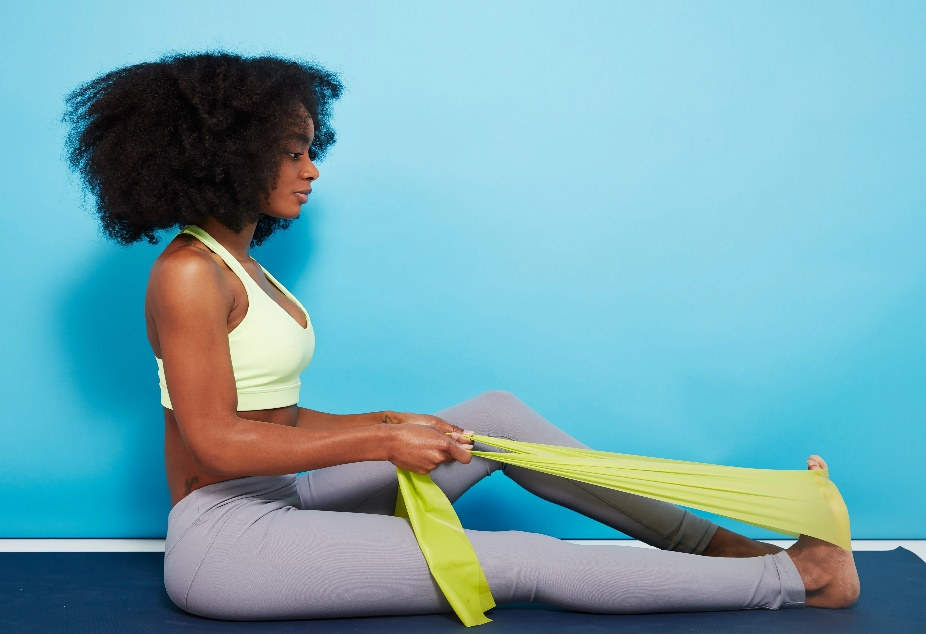

Knee Extension
Performing knee extension is one of the least invasive exercises that is helpful for this injury. It is a simple exercise that will not require much effort but whose result will be very favorable for your knee.
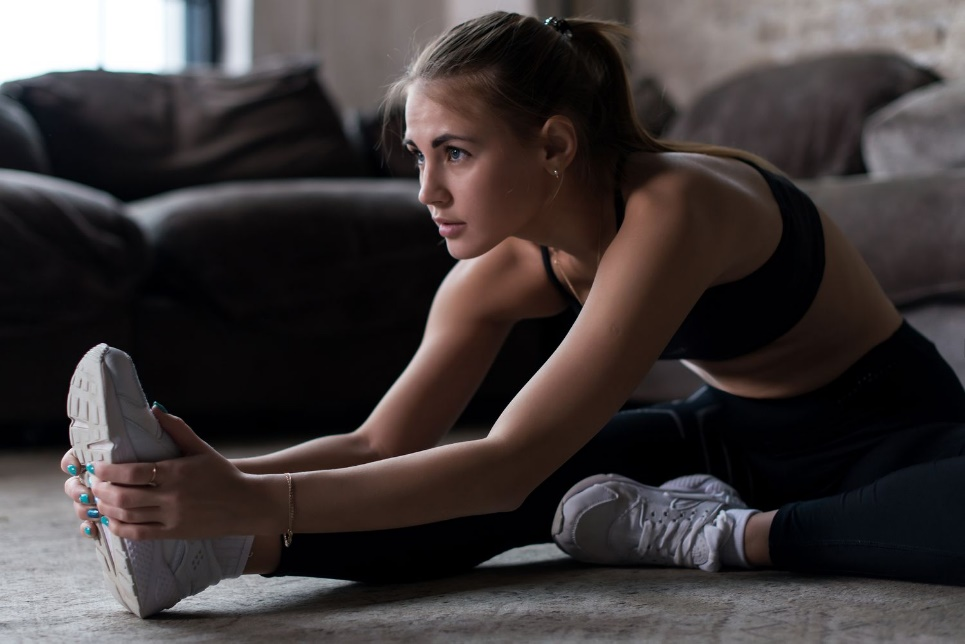
Thigh Stretch
The thigh stretch is one of the best exercises for a medial meniscus tear. In addition, you can easily do it in the comfort of your home without any extra instrument or device.

Pelvic Lift
In the pelvic elevation exercises we also find a slight movement of the knees that implies a little weight. Hence, it is also recommended to treat this lesion.
Heel Lift
When performing heel lifts we are also performing meniscus injury exercises. The impact is slight, so it will cause less discomfort when doing it, but it will certainly be of great help.
How Long Does It Take for a Torn Meniscus to Heal Without Surgery?
Usually, your physician or physical therapist in Manchester will ask you to diminish your sports activities meanwhile your meniscus tear heals. This healing process might take from four up to eight weeks. According to an article posted by (Rachel M. Frank) this will be depending on the complexity and place of the tear. When this period is being carried out you should do strength training in order to strengthen your core and buttocks muscles.
References
D’Ambrosi, R., Meena, A., Raj, A. et al. In elite athletes with meniscal injuries, always repair the lateral, think about the medial! A systematic review. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 31, 2500–2510 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-022-07208-8
Luvsannyam E, Jain MS, Leitao AR, Maikawa N, Leitao AE. Meniscus Tear: Pathology, Incidence, and Management. Cureus. 2022 May 18;14(5):e25121. doi: 10.7759/cureus.25121. PMID: 35733484; PMCID: PMC9205760.
Baker BE, Peckham AC, Pupparo F, Sanborn JC. Review of meniscal injury and associated sports. Am J Sports Med. 1985 Jan-Feb;13(1):1-4. doi: 10.1177/036354658501300101. PMID: 3838420.
Fox AJ, Bedi A, Rodeo SA. The basic science of human knee menisci: structure, composition, and function. Sports Health. 2012 Jul;4(4):340-51. doi: 10.1177/1941738111429419. PMID: 23016106; PMCID: PMC3435920.
Hanna T, Smith NP, Sebastianelli WJ. Treatment, Return to Play, and Performance Following Meniscus Surgery. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2022 Jun;15(3):157-169. doi: 10.1007/s12178-022-09754-7. Epub 2022 Apr 25. Erratum in: Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2022 Jul 26;: PMID: 35467166; PMCID: PMC9107559.

