Traditional Medicine : Wet vs Dry Cupping Therapy
The Therapeutic Spectrum of Cupping Therapy: Dry vs. Wet Cupping in Modern Practice
Cupping therapy, a revered practice rooted in traditional medicine, has transitioned seamlessly into contemporary therapeutic settings. Its two main variants, dry cupping and wet cupping, offer distinct yet overlapping benefits. This article delves into their mechanisms, evidence-backed benefits, and critiques to guide both practitioners and patients in their application.
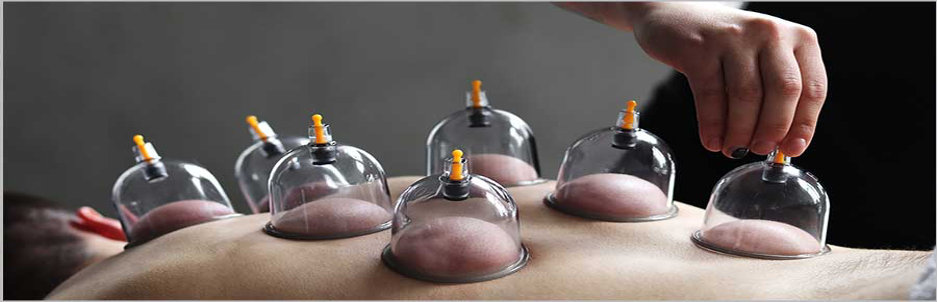
What is Dry Cupping?
Dry cupping involves the application of cups to the skin, where a vacuum is created to lift underlying tissues without incisions. It is celebrated for its non-invasive nature and is primarily used to:
- Alleviate muscle tension
- Improve blood circulation in localized areas
- Manage mild to moderate pain
How It Works:
- Localized Blood Flow: The suction enhances oxygen delivery to tissues.
- Pain-Gate Mechanism: Stimulates large nerve fibers to block pain signals.
- Fascial Release: Reduces tightness in connective tissues, enhancing mobility.
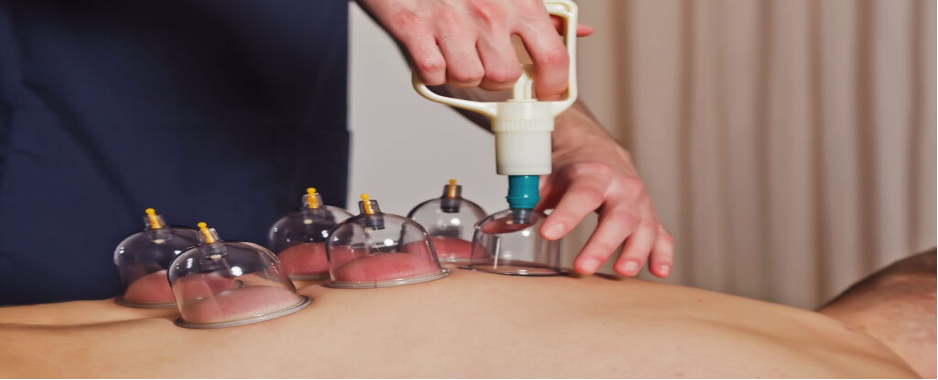
What is Wet Cupping?
Wet cupping, or “hijama,” incorporates small incisions on the skin to draw blood along with suction. This process is believed to remove toxins, stagnant blood, and inflammatory byproducts, making it effective for:
- Detoxification
- Treating systemic inflammation
- Chronic pain management
How It Works:
- Toxin Extraction: Eliminates oxidative stress markers and inflammatory mediators.
- Immune System Activation: Stimulates immune responses for systemic healing.
- Endogenous Opioids: Incisions promote the release of natural pain-relieving substances.
Clinical Efficacy: Comparing Dry and Wet Cupping
Research on Dry Cupping
- Chronic Pain Relief:
- Kim et al. (2020) found dry cupping significantly reduced lower back pain and improved mobility in a controlled trial.
- Wang et al. (2022) highlighted its role in sports recovery, enhancing muscle oxygenation and flexibility.
- Enhanced Circulation:
Studies indicate improved blood flow aids in soft tissue repair, making it suitable for acute injuries and rehabilitation.
Research on Wet Cupping
- Inflammation Reduction:
- El Sayed et al. (2020) noted a decrease in C-reactive protein levels, a marker of inflammation, after wet cupping sessions.
- Zarei et al. (2021) demonstrated significant improvement in rheumatoid arthritis symptoms.
- Neurological Benefits:
- Arslan et al. (2018) reported reduced migraine severity and frequency, suggesting its neurological effects may extend beyond pain relief.
Key Differences and Applications
| Aspect | Dry Cupping | Wet Cupping |
| Invasiveness | Non-invasive | Involves minor incisions |
| Primary Mechanism | Improves local circulation | Removes toxins and inflammatory markers |
| Therapeutic Focus | Muscle recovery, pain management | Detoxification, systemic inflammation |
| Risk Profile | Minimal risks | Requires hygiene to prevent infections |
Critiquing the Evidence: Strengths and Weaknesses
Dry Cupping: Benefits and Limitations
- Strengths: Non-invasive and accessible; minimal downtime.
- Critiques: Evidence often lacks rigorous controls, and placebo effects can influence subjective outcomes like pain perception.
Wet Cupping: Promises and Challenges
- Strengths: Effective for systemic conditions; demonstrated impact on inflammatory markers.
- Critiques: The invasive nature raises concerns about safety and practitioner expertise. The detoxification hypothesis requires more biochemical validation.
Mechanistic Insights: What Happens in the Body?
Dry Cupping:
- Enhances lymphatic drainage, aiding in waste removal.
- Triggers mechanoreceptor stimulation, reducing pain perception.
Wet Cupping:
- Stimulates bloodletting, potentially reducing oxidative stress.
- Activates immune modulators, improving systemic resilience.
When to Choose Dry or Wet Cupping?
Dry Cupping is Ideal for:
- Acute muscle tightness or spasms.
- Patients seeking a non-invasive introduction to cupping.
Wet Cupping Suits:
- Chronic inflammatory conditions like arthritis.
- Patients seeking traditional detoxification therapies.
Integration into Holistic Treatment Plans
To maximize therapeutic outcomes, consider combining cupping therapy with complementary interventions:
- Physical Therapy: To enhance musculoskeletal rehabilitation.
- Acupuncture: To target systemic conditions holistically.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Including hydration and diet to support detoxification.
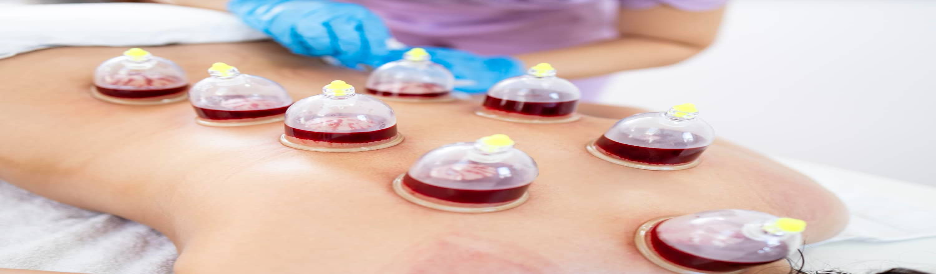
Conclusion: Tailored Applications for Optimal Results
Dry and wet cupping represent two sides of a therapeutic coin, each offering unique benefits tailored to specific conditions. While dry cupping shines in musculoskeletal recovery, wet cupping provides systemic relief for chronic conditions. Leveraging these modalities based on individual needs ensures optimal health outcomes backed by evidence and tradition.
Book A Consultation With our Naturopathic Therapist Practitioner below:
