
Shoulder Labrum Tears
A SPORTS PHYSIOTHERAPY OVERVIEW OF TREATMENT, PREVENTION & MANAGEMENT OF LABRAL TEARS FACTORING SHOULDER INSTABILITY & NON-SURGICAL PAIN MANAGEMENT
The Shoulder Labrum Tear, as the name suggests, is a painful and limiting condition caused by a tear in the thick piece of tissue attached to the edge of the shoulder.
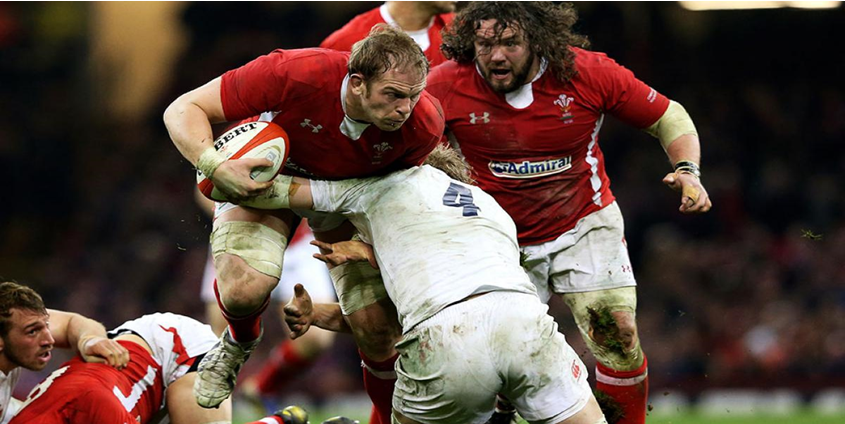
Research studies have been shown that Shoulder Labral Injuries have a prevalence rate of 0.12 per 1000 exposures; in this sense, elite athletes are highly susceptible to sustain these types of shoulder disabilities resulting in instability due to collision over the shoulder, and persistent traumatic events, is worth keeping in mind that overhead and contact sports such as baseball, cricket, rugby, volleyball, American Football, and other overhead arm motions activities similar to throwing are tending to generate the Shoulder Labral Injury , reports (Sandeep Mannava MD et la, 2018).

The Shoulder labrum, as we have just mentioned, outlines and covers the entire surface of the shoulder joint and also reinforces the socket and ball of said joint (Cooper De et al, 1992).
The shoulder joint is made up of the glenoid, which is the shallow depression of the socket, and the head of the upper forearm known as the humeral head, that is the ball which inserts into the socket, explains (Stephen Fealy MD, 2020).
Johns Hopkins says, there are three ways this piece of tissue can be torn, the 1st is completely outside the bone, the 2nd way is where the tendon of the biceps muscle is attached, and the 3rd can bring about both ways within and along the edge of the labrum. Which is why a physical examination and assessment is essential to diagnose alongside MRI Screening to accurately determine the complexity of injury.
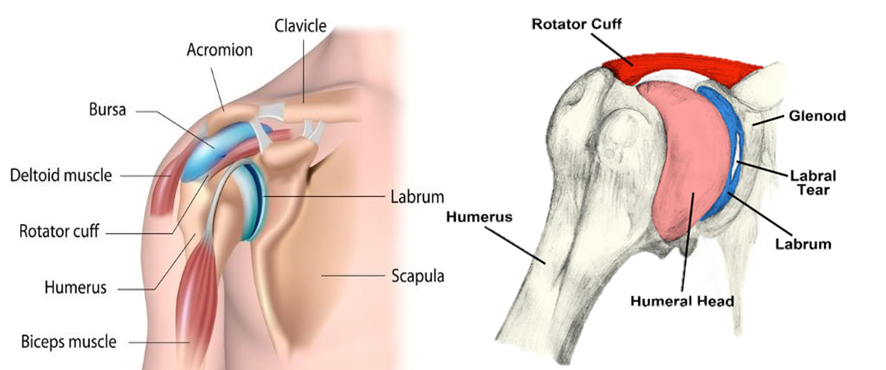
A research article posted by Hospital for Special Surgery (HSS) indicates the labrum is essential in the fixation of the shoulder because it has many ligament attachment sites which provide support to the joint; the most common are the rotator cuff and several muscles that enclose the shoulder which prevent the shoulder from dislocating.

SO, WHAT DOES A TORN SHOULDER LABRUM ACTUALLY FEEL LIKE?
Most commonly symptoms of a torn shoulder are intense sharp shoulder pain, achiness in the joint, instability and a feeling of grating, grinding, locking, and catching while performing shoulder movements.
Patients who usually suffer from this condition usually report deep pain in the shoulder joint accompanied by a popping sensation and instability to hold the arm in specific positions.
According to Rebound, the most common Shoulder Labrum Tear Symptoms are:
- Instability in the shoulder.
- Deep pain in the joint.
- Popping and Clicking Sensation.
- Discomfort or pain when lifting objects or moving the arm.
- Reduced ROM.
- Weakness in the Shoulder joint, on numerous occasions on one side.
These symptoms vary depending on what type of labrum tear the patient has suffered, they’re described below.
WHAT ARE THE DIFFERENT TYPES OF SHOULDER LABRAL TEARS?
The two most common types of labral injuries are the SLAP tear and Bankart tear. Both types of tears are usually accompanied by aching pain and difficulty performing normal shoulder movements.
What are SLAP tears?
SLAP acronym means “Superior Labrum Anterior to Posterior”. The part affected in this type of tear is the front area of the upper arm where the biceps tendon connects with the shoulder.
Baseball pitchers and volleyball players who perform high-energy, quick-snap actions across the top of the musculoskeletal area of the shoulder are the most vulnerable to this injury.
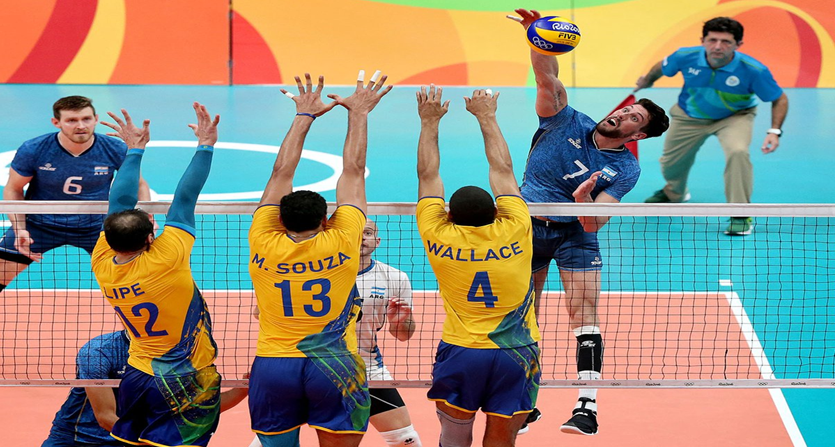

Patients with SLAP tears may present pain close to the biceps tendon in the front of the shoulder. The anterosuperior labrum usually appears to have a poor blood supply, whereas the inferior labrum has a significant blood flow (Cooper DE et al, 1992).
How incident is the SLAP in the population?
Even today the incidence of this condition is a matter of debate; it is known that Snyder has stated on different occasions that the percentage has been growing exponentially hard in the last decades. Proof of this are the studies carried out in 2002 where the incidence in the population was 4 out of every 100,000 people and in 2010 where the incidence increased to 22.3 out of every 100,000 people. Another characteristic of this condition is that the highest incidence usually occurs in young patients between 20 and 29 years of age and between the ranges from 40 to 50 years, lays out (Scott D. Mair et la, 2021).
What are Bankart tears?
Bankart tears are most common in younger subjects who have had their shoulder dislocated. The joint capsule (fibrous tissues that surround, support, and keep safe the joint) can pull on the lower portion of the labrum and tear it if the ball of the shoulder joint falls out of the socket. As a result of the labrum rupture, the shoulder is more likely to re-dislocate, causing instability.
Anterior instability is caused by a dislocation in which the head of the humerus slips toward the front of the body, and its lifetime reoccurrence is nearly from 1% up to 2%, claims (Matthew Varacallo et al, 2021).
Posterior instability occurs when the ball slips toward the back of the body, it should be noted that this particular one is an odd condition as it represents 10% incidence of all existing shoulder injuries, apprises (Alaina Brelin et al, 2017). The affected individuals with Bankart tears may be concerned that the shoulder will dislocate or slip out of place.
ARE ATHLETES THE MOST PRONE TO SHOULDER LABRAL INJURY AND CAN SHOULDER LABRUM TEAR BE PREVENTED?
Normally this condition is quite difficult to prevent, unfortunately high performance athletes are predisposed to have it as this condition is sensitive to overhead movements.
However, people who have suffered from a traumatic event such as a fall are also prone to experience it. Older adults are also at risk for this injury as these tissues become more fragile with aging, as well as tissue degeneration caused by recurring overhead manual labourer occupations, points out (David C et la, 2021).
Although SLAP is difficult to prevent there are certain methods that can help prevent it. As we mentioned earlier, athletes are more likely to develop this affection, especially baseball and softball pitchers due to overuse of movement in the shoulder. Monitoring and limiting the pitch count especially in a young pitcher can be a good precaution method against this condition, affirms (John Henry Wilckens, MD).
CAN A SHOULDER LABRAL TEAR HEAL WITHOUT SURGERY?
Initial treatment for shoulder labrum tear & for SLAP usually does not require surgical intervention; initially Physical Therapy Manchester is used depending on the severity of the tear. “Surgeons should try to be as conservative as possible when treating a torn shoulder labrum,” says Dr. Fealy.
Surgeons will usually conduct a physical clinical assessment and order MRI or X-ray to determine which the appropriate treatment for the patient is. Sports Physiotherapy Manchester is usually accompanied by anti-inflammatories, and, in specific cases, cortisone injections for Shoulder Labral Injury can also be used. Gradual shoulder extensions performed by a physical therapy Manchester practitioner over a period of one to two months should also be added.
For this reason is essential to seek out and turn up to your Physiotherapy Manchester practitioner in order to assess your condition with the shoulder labrum tear test, feel free to contact us www.mysportsinjury.co.uk
HOW LONG DOES THE SHOULDER LABRUM TEAR INJURY TAKE TO BE SOLVED UNDER MY SPORTS INJURY CLINIC PHYSIOTHERAPY MANCHESTER MANAGEMENT PROGRAM?
The required recovery time frame to rehab a torn labrum could approximately take from 2 months up to 3 months, in this case scenario is paramount the physiotherapy guidance of your Sports Massage Manchester clinicians, explains MorePhysicalTherapy.
WHEN DO YOU NEED SURGERY FOR A TORN SHOULDER LABRUM?
Surgical treatment should be considered when all non-conservative methods have been tried without efficacy. The type of intervention that will be performed on the patient will depend on the severity of the tear. “If physical therapy fails and the athlete still can’t complete overhead motions, or the shoulder continues to dislocate, surgical treatment might be required to reattach the torn ligaments and labrum to the bone,” says Dr. Fealy.
Russel Warren, MD, for Arthroscopic procedures sets out that one of the most used methods to treat SLAP is arthroscopy, since when carried out through a small incision it is much less invasive than an open operation.
Doctors usually recommend more conservative methods for older people who do not perform physical activity on a regular basis; otherwise young athletes are usually managed through arthroscopic surgery to achieve greater efficiency. Find the best Sports physiotherapist in Manchester to treat your Labral Tear Condition.
WHAT IS THE RECOVERY TIME FRAME FOR SHOULDER LABRUM TEAR SURGERY?
Recovery from surgery depends on different factors such as the specific location of the tear and how good the surgical intervention was. Regularly, the recovery period after undergoing surgery varies from 4 up to 5 weeks when the labrum begins to adhere to the edge of the bone again and it could take twice time period time for it to fully strengthen. In athletes the period is much longer because they will need from 6 months to a year to fully recover.
Patients are usually recommended to wear a sling for four weeks after the operation, regardless of the surgery performed. This helps protect the shoulder while it heals during the post-operative period. In parallel, the recovery process must be accompanied by a Sports Physical Therapist including custom counselling in order to return a full function and live pain-free.

The average time of returning to sports and getting back on daily basis activities after arthroscopic SLAP repair surgery ranges from 8 up to 9 months and the success rate accounts for 69.9% of screened individuals who got back their optimal level and proficiency, says (Aarabi Thayaparan et al, 2019).
SHOULDER LABRAL TEAR EXERCISES RECOMMENDED BY YOUR SPORTS MASSAGE MANCHESTER CHIROPRACTORS
If arthroscopic surgery is indicated in a SLAP injury, the Physical Manual Therapist must design a program for shoulder rehabilitation including shoulder labral tear exercises, starting with a functional assessment, subsequently; pain treatment, passive / active mobilisations, is important avoid Adhesive Capsulitis of the Shoulder (prolonged immobilization), adjacent trigger point treatments, and Neurodynamic exercises.
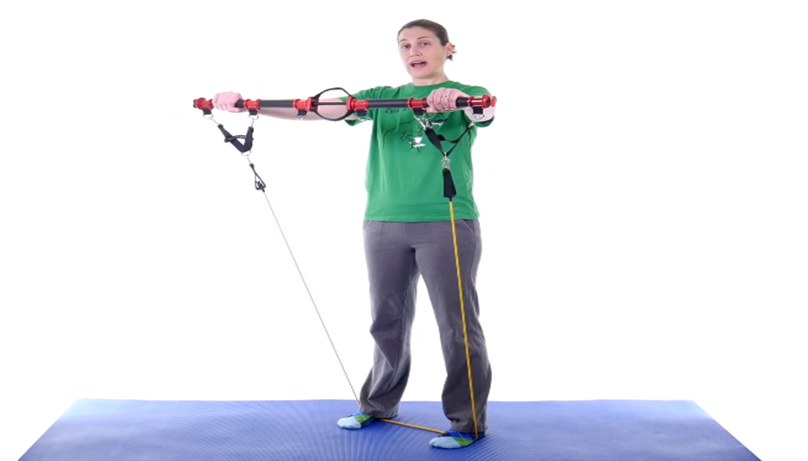
- Toning or strengthening exercise for recovery from shoulder injuries
These are exercises to strengthen or tone the rotator muscles of the shoulder, supraspinatus, infraspinatous, and rotator cuff. In addition, the posterior muscles of the arm as well.
Use a rubber band, dumbbell, perform a short contraction, take a break between contractions of at least 3-4 seconds, it can be done several times a day.

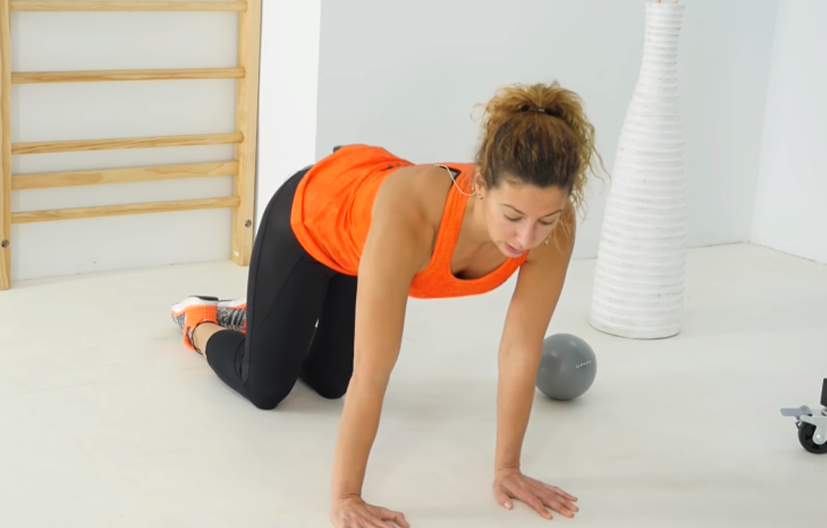
- Stabilisation exercises for shoulder injuries and rehabilitation
We show you a series of exercises indicated to stabilise the shoulder joint, recommended in cases of shoulder rehabilitation in injuries where stability is affected.
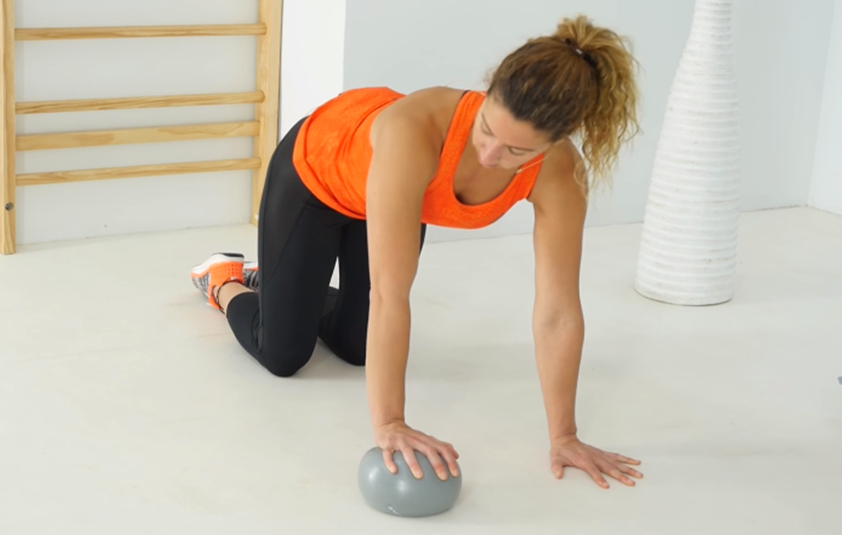
Kneel on and put your hands on the floor like a cat-cow position and start making circles in that position in order to give a little loads to the injured shoulder so the musculoskeletal area actives and stabilise itself.

You can also add an unsteady object to the routine like a ball; this exercise can be performed several times a day as well.

- Exercises to improve shoulder mobility
We give you various recommended exercises to improve and regain mobility of the shoulder joint complex.
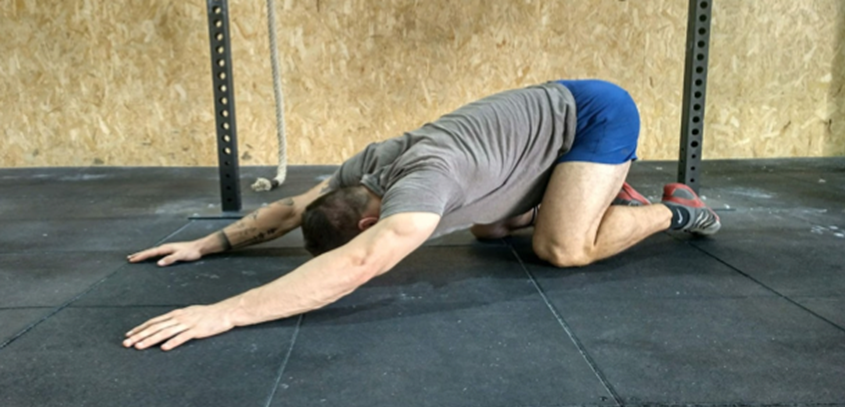
Kneeling, we place our hands and head resting on the floor with our arms extended above our heads. We should feel a stretch in the shoulder or upper or lower back.

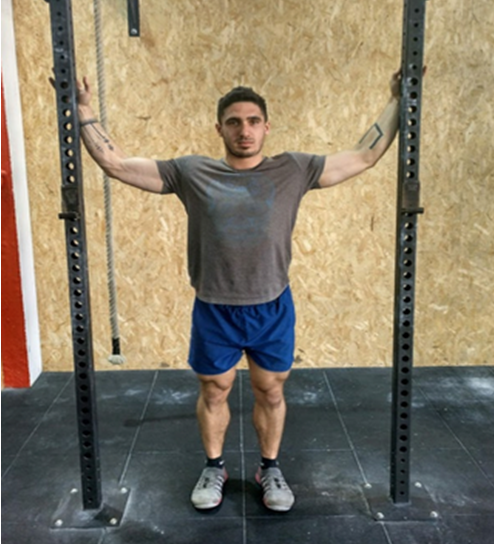
We stand in a narrow squat rack or under a door frame and place the hand and forearm on each side of the structure. Keeping the arms in that position, we advance the torso until we feel a stretch in the pectoral or shoulder area.

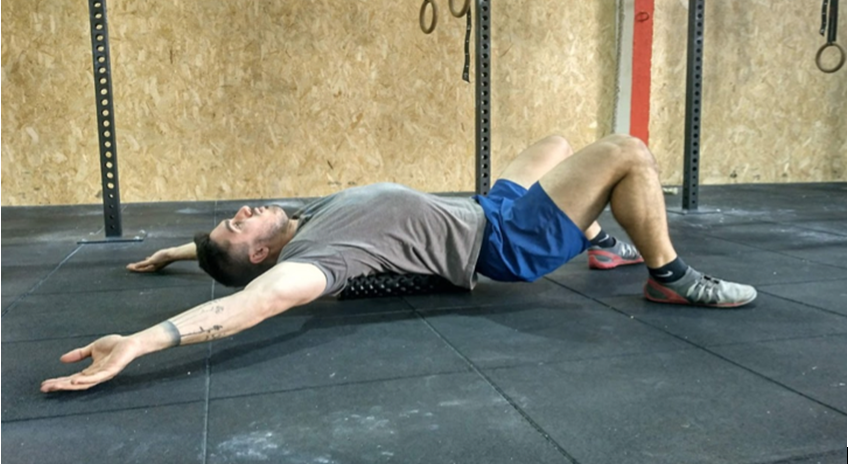
We lie on the floor on our back with a mobility roller under the centre of the back longitudinally, or some other structure that raises our back without hindering movement. We place the arms extended to the sides of the body with the palms facing the ceiling. From that position we slide the backs of the hands up to the top of the head and return to the starting point. We should feel a stretch in the chest area and / or in the anterior shoulder area.

KEY POINTS ABOUT SHOULDER LABRUM TEAR
The shoulder is one of the most important regions of our body and at the same time, one of the most affected parts since it suffers a lot of wear and tear on a day-to-day basis. You might think that this deterioration occurs mainly in athletes, but contrary to what people believe, anyone can have shoulder problems due to a fall or a repetitive activity in which the arm has to be raised overhead. These two factors can lead to a tear in the labrum, that is, a partial tear in the cartilaginous ring that surrounds the base of the shoulder joint and provides it with stability.
There are two types of tears. Traumatic tear of the labrum; athletes are very prone to suffering from it. It occurs mainly for these reasons due to a shoulder dislocation and also for an injury as a result of lifting heavy objects or high impact activities. The other one is non-traumatic tear of the labrum; it occurs in people with great laxity, since they have greater mobility in the shoulder joint. It is precisely this joint instability of the shoulder or muscle weakness that causes tears.
Many times this condition is asymptomatic, especially when it is a small tear, so it does not cause pain.
To find out if a labrum tear is suffered, the sports physiotherapy Manchester practitioner will perform the shoulder labrum tear test that assess the labrum and the stability of the shoulder joint, and an MRI may be also prescribed.
Depending on the type of tear, it can be treated with physical therapy that will plan a rehabilitation and prevention treatment for certain movements and positions, perform manual therapy to reduce pain and correct movement, do exercises to strengthen the shoulder, balance the muscles, reduce pressure on the labrum and do stretching. Likewise, the physiotherapist will help those who have undergone surgery through progressive rehabilitation exercises to prevent the tissues from tearing again.
Published by Rafael Peña for www.mysportsinjury.co.uk
References
- Mannava S, Frangiamore SJ, Murphy CP, et al. Prevalence of Shoulder Labral Injury in Collegiate Football Players at the National Football League Scouting Combine. Orthop J Sports Med. 2018;6(7):2325967118783982. Published 2018 Jul 9. doi:10.1177/2325967118783982
- Thayaparan A, Yu J, Horner NS, Leroux T, Alolabi B, Khan M. Return to Sport After Arthroscopic Superior Labral Anterior-Posterior Repair: A Systematic Review. Sports Health. 2019 Nov/Dec;11(6):520-527. doi: 10.1177/1941738119873892. Epub 2019 Oct 4. PMID: 31584340; PMCID: PMC6822213.
- Cooper DE, Arnoczky SP, O’Brien SJ, Warren RF, DiCarlo E, Allen AA. Anatomy, histology, and vascularity of the glenoid labrum. An anatomical study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1992 Jan;74(1):46-52. PMID: 1734013.
- Varacallo M, Musto MA, Mair SD. Anterior Shoulder Instability. [Updated 2021 Jul 18]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2021 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK538234/
- Brelin A, Dickens JF. Posterior Shoulder Instability. Sports Med Arthrosc Rev. 2017 Sep;25(3):136-143. doi: 10.1097/JSA.0000000000000160. PMID: 28777216.
